K-Means
- Clustering algorithm
- Number of clusters is a hyper-parameter
Algorithm
- Start with K random centroids (points in
- Repeat until convergence:
- Assign each point of the data to its closest centroid
- Replace current centroids with the mean of the points in the corresponding cluster
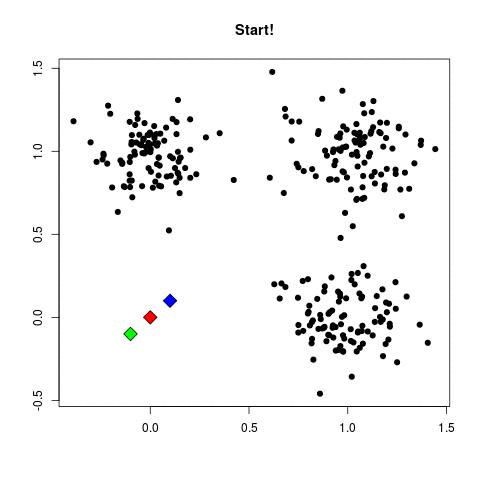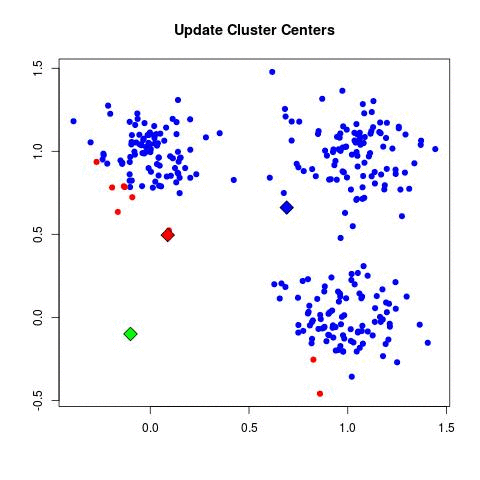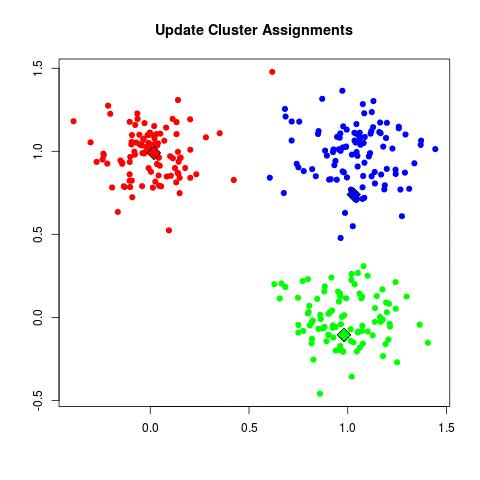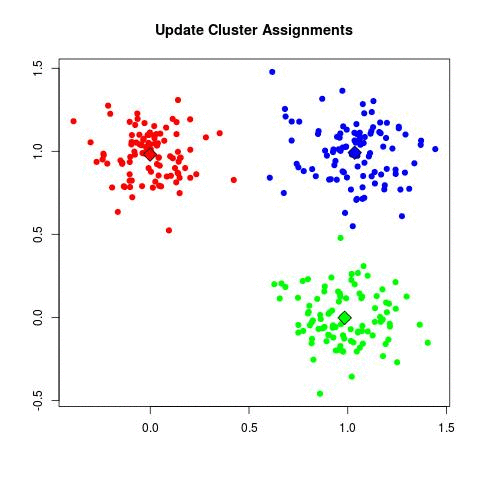
source: https://www.maartengrootendorst.com/assets/images/posts/2019-07-30-customer/kmeans.gif
Pros
- Easy to implement
- Easy to interpret
Cons
- Susceptible to correlated features
- Susceptible to features with different variances