Recurrent Neural Network
A Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) is a type of artificial neural network designed for sequential data processing. Unlike traditional feedforward neural networks, RNNs have connections that form cycles, allowing them to maintain hidden states and capture temporal dependencies in sequential inputs. RNNs are well-suited for tasks such as natural language processing, time series analysis, and any problem involving sequential patterns, where the order of input elements matters. However, traditional RNNs can face challenges like difficulty in learning long-term dependencies.
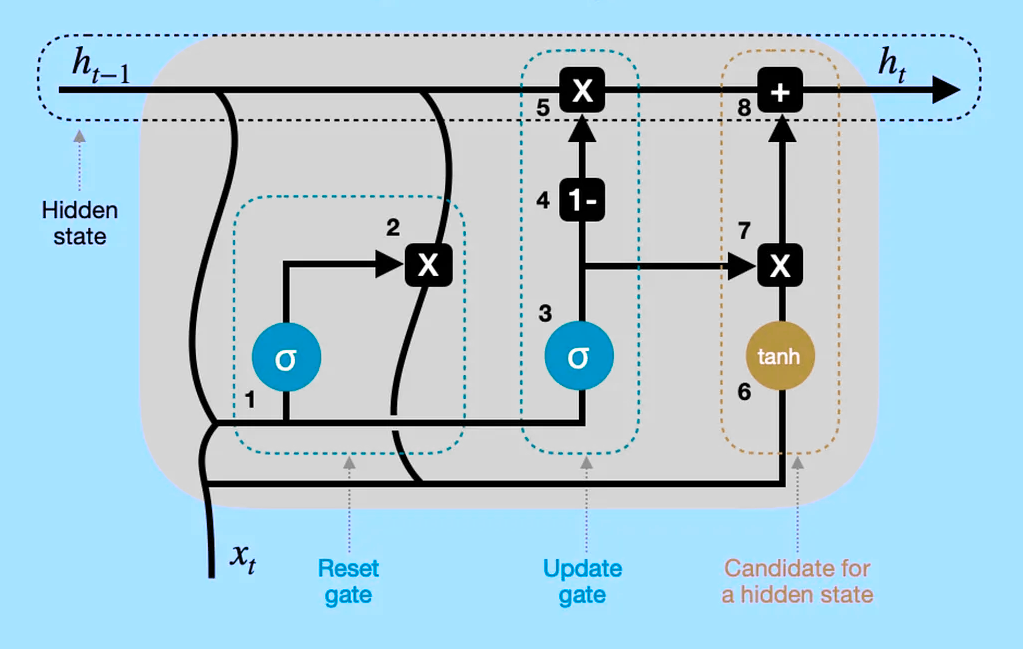
General architecture
 source: Wikipedia
source: Wikipedia
Standard Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) suffer from short-term memory due to a vanishing gradient problem that emerges when working with longer data sequences. Two popular methods try to address this issue.
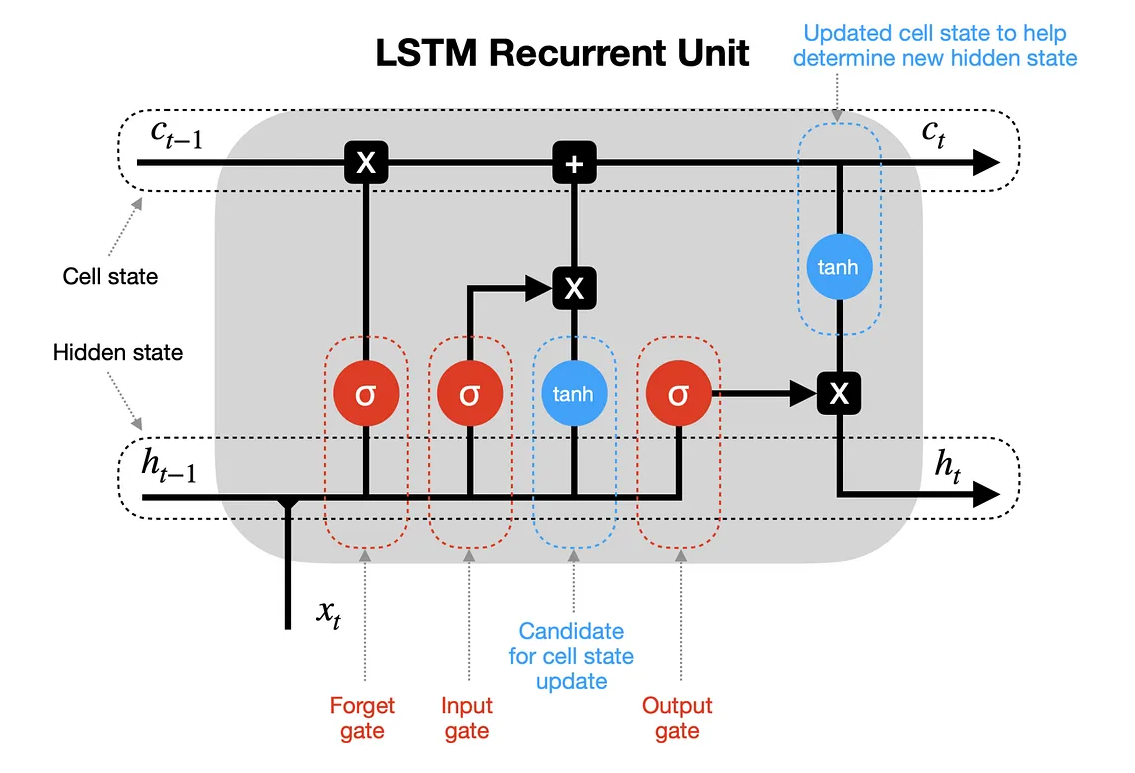
Long Short-Term Memory (LTSM)
LSTMs introduce memory cells and gating mechanisms that allow the network to selectively remember or forget information over extended sequences. This makes LSTMs particularly effective for tasks involving long-range dependencies, such as natural language processing, speech recognition, and time series prediction. The architecture's ability to handle vanishing and exploding gradient problems makes it well-suited for learning from sequences with extended context.
Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU)
Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) is another type of recurrent neural network (RNN) architecture, similar to LSTM but with a simpler structure. GRUs also aim to address the vanishing gradient problem and capture long-term dependencies in sequential data. They feature gating mechanisms that control the flow of information, including an update gate and a reset gate. The update gate regulates the amount of information carried over from the previous hidden state, while the reset gate controls how much past information to forget. GRUs offer computational efficiency and competitive performance compared to LSTMs, making them suitable for various sequential tasks, especially in scenarios where computational resources are a consideration.