Perceptron
A perceptron is a basic unit of a neural network and serves as a simple model of a biological neuron. It takes multiple binary inputs, applies weights to these inputs, sums them up, and passes the result through an activation function to produce an output. The perceptron is the fundamental building block for more complex neural network architectures. It was introduced by Frank Rosenblatt in the late 1950s and forms the basis of single-layer neural networks.
Mathematical framework
A perceptron is an artificial neuron with a Heaviside activation function.
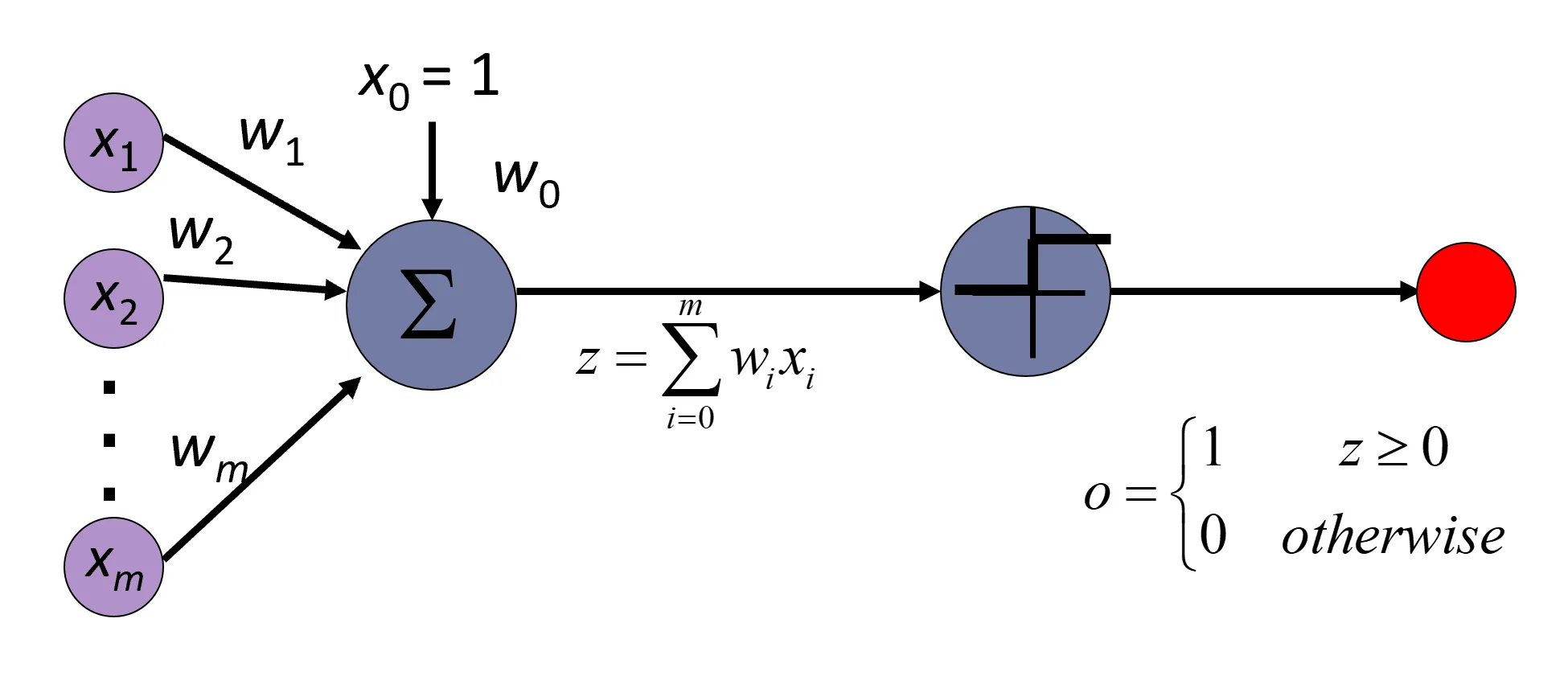 image source : https://towardsdatascience.com/perceptrons-the-first-neural-network-model-8b3ee4513757
image source : https://towardsdatascience.com/perceptrons-the-first-neural-network-model-8b3ee4513757
A perceptron is just an indicator function that returns
Nowadays, activation functions are usually RELU or sigmoid.