Fine-tuning and resampling
When assessing a machine learning model, it's common to divide the dataset into three parts: training set, validation set, and test set. Each set serves a specific purpose in training, fine-tuning, and evaluating the model, and this division helps ensure the model's performance generalizes well to unseen data. Here's why each set is important:
- Training Set:
- Purpose: The training set is used to train the model. The model learns patterns, relationships, and features from this set.
- Training Process: The model's parameters (weights and biases) are adjusted based on the input-output pairs in the training set.
- Role: The training set helps the model to learn the underlying patterns in the data and build a representation that can make accurate predictions.
- Validation Set:
- Purpose: The validation set is used during the training process to fine-tune the model and optimize hyperparameters.
- Hyperparameter Tuning: As the model trains on the training set, its hyperparameters are adjusted based on how well it performs on the validation set. This helps prevent overfitting and ensures the model generalizes well to new, unseen data.
- Role: The validation set serves as an unbiased evaluation during the model development phase, guiding adjustments to improve performance.
- Test Set:
- Purpose: The test set is reserved for evaluating the model's performance after it has been trained and fine-tuned.
- Unseen Data Evaluation: The test set contains data that the model has never seen during training or validation. It provides an unbiased assessment of how well the model generalizes to new, unseen data.
- Role: The test set helps estimate the model's performance in real-world scenarios and ensures that the evaluation is not biased by the training or validation data.
Resampling techniques
Validation set
Split the dataset in two parts. Typically keep 60% to 80% to train the model.
Leave-One-Out Cross-Validation
Exclude one observation from the dataset and train the model on the remaining observations. Repeat for all observation and estimate the error by averaging.
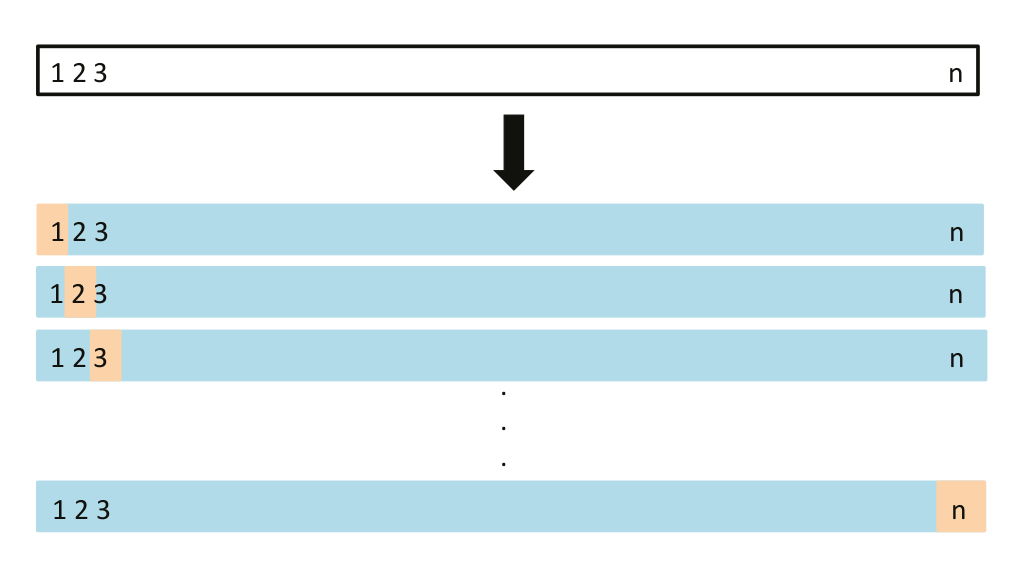
source: #ISLP
Shuffle then split the dataset into
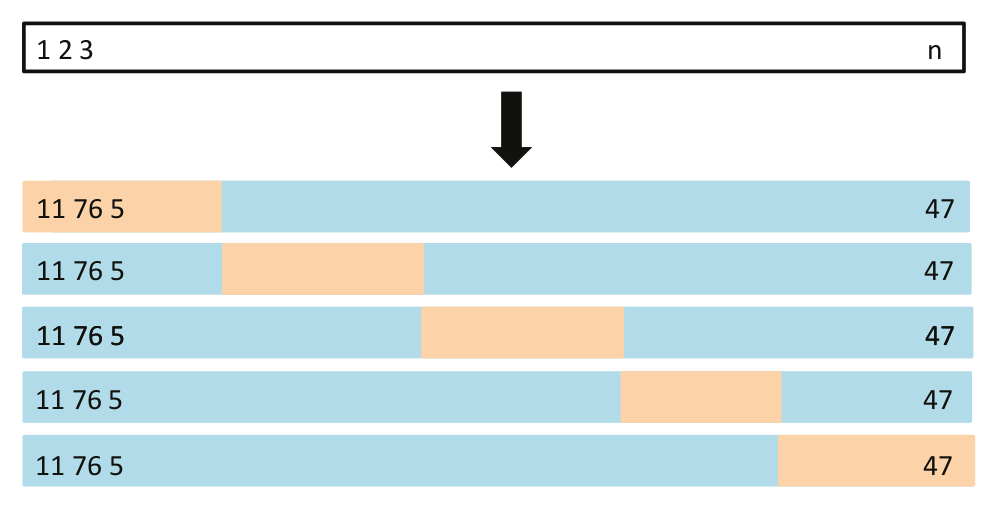 source: #ISLP
source: #ISLP