Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
A GAN is a type of artificial intelligence model that consists of two neural networks, a generator, and a discriminator, engaged in a competitive learning process. The generator creates synthetic data, such as images, while the discriminator evaluates the authenticity of the generated data compared to real data. The two networks iteratively refine their performance through adversarial training, where the generator aims to produce increasingly realistic data to deceive the discriminator, and the discriminator strives to accurately distinguish between real and generated data. This dynamic competition results in the generation of high-quality, realistic data by the generator, making GANs widely used in image, video, and content synthesis applications.
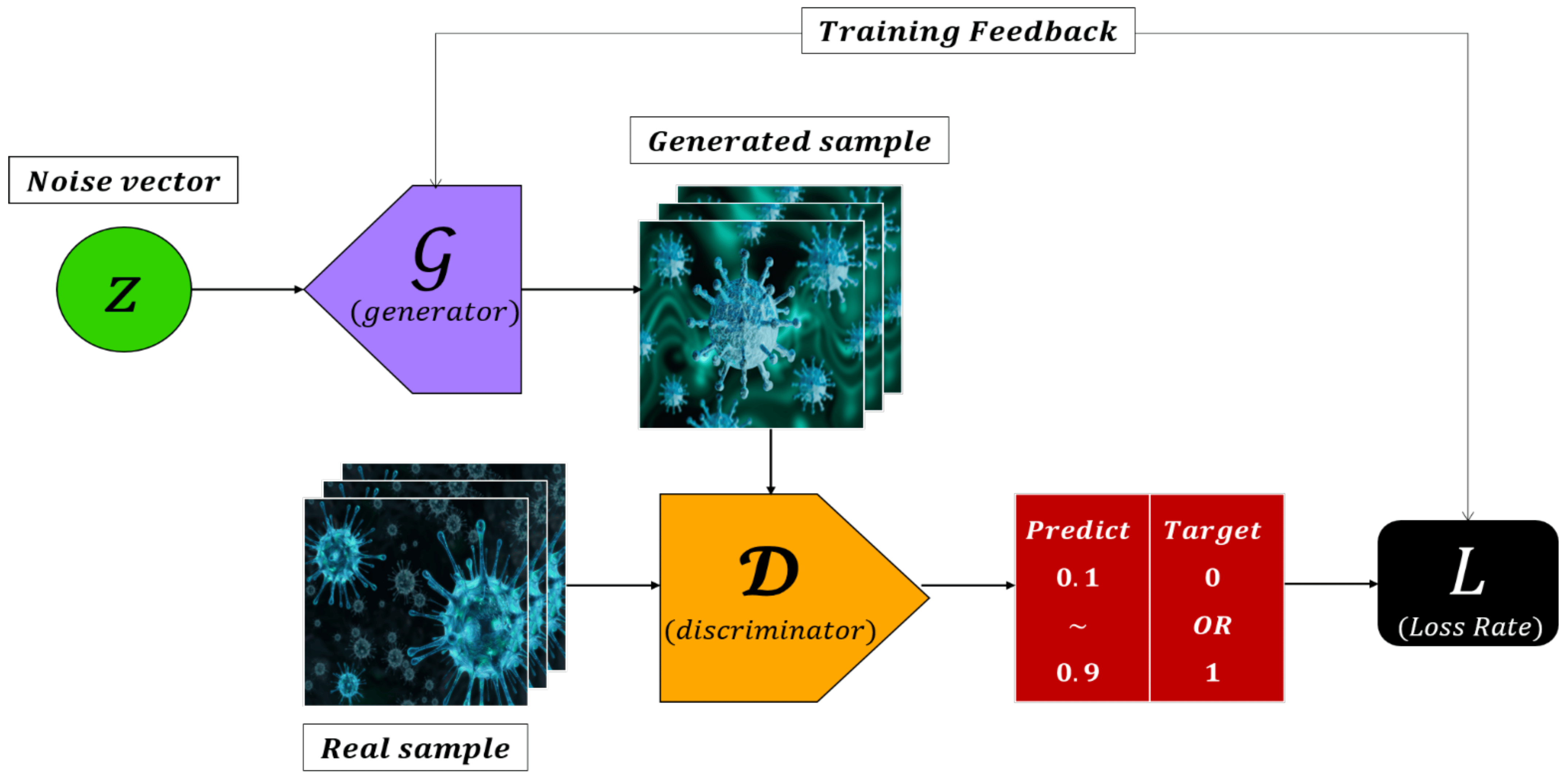
source : https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9292/10/10/1216
Pros
- High-Quality Data Generation: GANs are capable of generating high-quality, realistic data, such as images, audio, and text, with diverse applications in creative fields.
- Unsupervised Learning: GANs excel in unsupervised learning scenarios, where the model can learn to generate data without explicit labels.
- Data Augmentation: GANs can be used for data augmentation, enhancing the size and diversity of training datasets, which is beneficial for improving the performance of other machine learning models.
- Creative Applications: GANs have been successfully applied in creative fields, including art generation, style transfer, and content synthesis.
Cons
- Training Instability: GANs are known for training instability, where the generator and discriminator may struggle to find an equilibrium, leading to mode collapse or poor convergence.
- Mode Collapse: GANs can suffer from mode collapse, where the generator produces a limited set of outputs, failing to capture the full diversity of the underlying data distribution.
- Hyperparameter Sensitivity: GANs are sensitive to hyperparameter choices, and finding the right configuration for stable and effective training can be challenging.
- Computational Resources: Training GANs requires substantial computational resources, particularly powerful GPUs, which may limit accessibility for some researchers or practitioners.
- Evaluation Challenges: Assessing the quality of generated samples and selecting appropriate evaluation metrics for GANs remains an open research challenge.