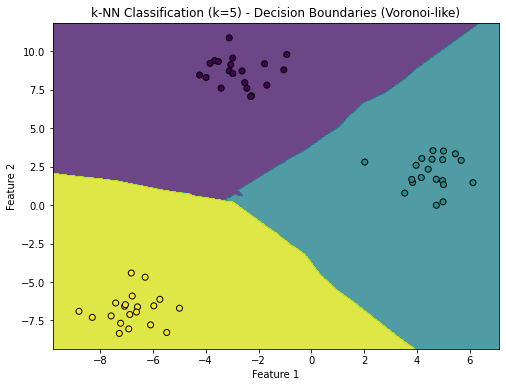
K-Nearest Neighbors
In statistics, the
- In
- In
Illustration
If